pop up description layer
HOME
Cryptozoology UFO Mysteries Aviation Space & Time Dinosaurs Geology Archaeology Exploration 7 Wonders Surprising Science Troubled History Library Laboratory Attic Theater Store Index/Site Map Cyclorama
Search the Site: |
|
How to Build a PyramidThe ancient Egyptians loved pyramids. There are sixty-seven, of various sizes, scattered around the city of Cairo alone. The most famous, and largest, are at Gizeh, where what is believed to be the three tombs of Khufu, Khafre, and Menkure, are lined up side by side. The end tomb, Khufu's, which is often referred to as "The Great Pyramid," just by itself is an impressive structure. It stood 480 feet tall when completed and contains twice as much volume as the Empire State Building. Until the 19th century it was the tallest building ever erected. Not bad for a structure 45 centuries old. So, how did the ancient Egyptians construct such an impressive monument so long ago? Some wild theories exist. Swiss Author Erick von Daniken suggested that aliens assisted the construction using advanced technology. Herodotus of Halicarnassus, a Greek writer who viewed the pyramids around 450 B.C. was told that giant machines were used to lift the blocks into place with the aid of 100,000 slaves working, for the entire year, for twenty years. Probably neither of these are correct. Most likely the Pharaoh employed a large work force, indeed as many as 100,000 men, but for only a fraction of the year. During the months of July, August, September and October, the Nile River flooded the land. This was actually a blessing for the Egyptian farmers as it allowed new fertile soil to be laid down over the fields. But it meant the farmers were unable to grow crops during this period. It is likely that the Pharaoh required his subjects to work on public projects, like the pyramids, during this season. Egyptian records indicate that the laborers, while being drafted against their will, were actually well cared for by ancient standards. Regulations have been found covering the maximum amount of work allowed per day, the wages received and holidays entitled to, each worker. By only requiring work to be done during flood periods, the Pharaoh could get a lot done without impacting the normal Egyptian economy. He probably also employed a much smaller work force year round on the project. Some would have been employed doing the skilled stonework while others planned and prepared the site for the laborers that would be available during the next flood season. The shape of the pyramid are the logical one for producing buildings of great height when the building material available is stone. The design mimics the natural geometry of a mountain, an incline of about 52 degrees. The Egyptian architects realized the ever widening base would easily support the increasing number of stone blocks above it making the structure very stable. An average 2 and 1/2 ton limestone block used in the pyramid construction would have probably taken 8 men nine or ten days to move from the quarry, float across the Nile, and drag to the top of the pyramid.
A more practical design would have been a spiral ramp going up around the pyramid. However, such an arrangement would have only allowed a narrow path to the top and the turns at each corner would have been difficult to negotiate while towing a 2 ½ ton stone. French architect Jean-Pierre Houdin advanced the theory that a spiral ramp was used on the inside of the pyramid to move the stone blocks. According to Houdin a straight external ramp was used to get materials to the 140 foot level. From there workers dragged the stones through a set of gently rising tunnels just inside the outer walls. The last tunnel would exit on the monument's top. A 1986 microgravity survey of the pyramid discovered a peculiar anomaly: a less-dense structure in the form of a spiral within the pyramid that may turn out to be what is left of Houdin's tunnels. Scientists are now seeking permission from the Egyptian government to do more non-invasive tests that would prove or disprove Houdin's theory. Whatever the shape of the ramps may have been topped with a surface of Tafla, a clay. Tafla, when wet, becomes very slippery and may have allowed the Egyptian builders to use shorter, steeper ramps than might have otherwise been possible. By wetting the ground in front of the block a slick path would be created allowing the stone to be dragged by rope as it sat on sledges. It is also possible the stones could have been moved on rollers. By placing rounded logs under the stone, crude wheels would have made the load easy to pull. Pictures inscribed on ancient monument walls, though, suggest the blocks were dragged without the aid of rollers. Once a stone was at the top of the pyramid, it was probably moved into its final position with the use of levers. We can see the Egyptains didn't become great pyramid builders right away. They needed some practice. They started by cutting tombs into the rock of the desert floor and building mastabas (from the Arab word meaning "bench") over them. Mastabas were raised, flat, platforms. Some were twenty-five feet high and two-hundred feet square. Imhotep, architect to the Pharaoh Zoser, changed this by building his king a mastaba and then placing another, smaller mastaba right on top of it. On top of that he placed another even smaller mastaba. When he was finally done the structure had six levels and resembled a stepped pyramid.
Without this trick and with a poor foundation, the pyramid at Meidum was easily shaken apart during earthquakes. Later, better built pyramids show that the Egyptians learned as they built and their masterpieces have stood the test of the centuries. Copyright Lee Krystek 1997. All Rights Reserved. |
|
Related Links |
|
|




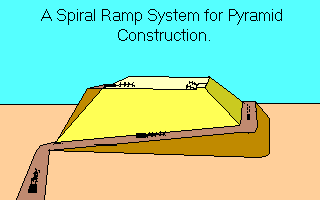 The
most likely method of getting the blocks to the top of the structure
was through massive construction ramps. Exactly how the ramps
were laid out is unknown and have been the source of heated debate
between archeologists for many years. A long straight ramp (as
pictured in the recent film 10,000 B.C.) seems to have
been too massive and impractical for something as big as the Great
Pyramid. To reach the top with a shallow enough grade to be able
to pull stones up it the ramp would have needed to be a mile in
length and contain a volume of material equal to that of the Great
Pyramid itself.
The
most likely method of getting the blocks to the top of the structure
was through massive construction ramps. Exactly how the ramps
were laid out is unknown and have been the source of heated debate
between archeologists for many years. A long straight ramp (as
pictured in the recent film 10,000 B.C.) seems to have
been too massive and impractical for something as big as the Great
Pyramid. To reach the top with a shallow enough grade to be able
to pull stones up it the ramp would have needed to be a mile in
length and contain a volume of material equal to that of the Great
Pyramid itself.
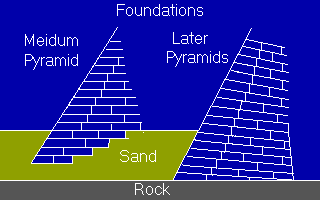 A
number of stepped pyramids were built after that, but the most
interesting is the one at Meidum built for Pharaoh Seneferu. It's
an example of an early design that failed. The pyramid, which
has four levels, is in near ruins today with many of its blocks
laying in a heap around the base. Why did it do so poorly when
many other pyramids are in much better shape? The architect of
this pyramid apparently had not yet learned the importance of
laying the foundation on solid rock rather than sand. Also, the
construction trick of tilting the blocks on a slope inward toward
the center of the pyramid had not been invented. By tilting the
blocks slightly inward, the weight of the blocks helped lock them
into the structure.
A
number of stepped pyramids were built after that, but the most
interesting is the one at Meidum built for Pharaoh Seneferu. It's
an example of an early design that failed. The pyramid, which
has four levels, is in near ruins today with many of its blocks
laying in a heap around the base. Why did it do so poorly when
many other pyramids are in much better shape? The architect of
this pyramid apparently had not yet learned the importance of
laying the foundation on solid rock rather than sand. Also, the
construction trick of tilting the blocks on a slope inward toward
the center of the pyramid had not been invented. By tilting the
blocks slightly inward, the weight of the blocks helped lock them
into the structure.
